What is difference within CMAT AND NMAT
The CMAT (Common Management Admission Test) and the NMAT (NMIMS Management Aptitude Test) are both entrance exams for management programs in India, but they are conducted by different organizations and have some differences in their structure and application process.
The CMAT is conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA) and is accepted by over 1000 management institutes across India. It is a three-hour computer-based test that assesses a candidate's ability in areas such as quantitative techniques, data interpretation, language comprehension, and logical reasoning.
The NMAT is conducted by the graduate management admission council (GMAC) and is specifically used for admissions to the management programs at NMIMS (Narsee Monjee institute of management studies) and several other leading Indian b-schools. It is also a computer-based test and assesses similar skills as the CMAT.
While both exams assess similar skills, they are administered by different organizations and have different sets of participating institutions. It's important for candidates to check the specific requirements of the programs they are interested in to determine which exam to take.

Certainly! Here are some additional details about the CMAT and NMAT:
- Eligibility Criteria:
- CMAT: To be eligible for CMAT, a candidate must hold a bachelor's degree in any discipline from a recognized university. There is no age limit to appear for the exam.
- NMAT: The eligibility criteria for NMAT may vary depending on the specific institute. Generally, candidates must have a bachelor's degree in any discipline with a minimum aggregate score of 50%. There is no age limit for NMAT.
- Exam Structure:
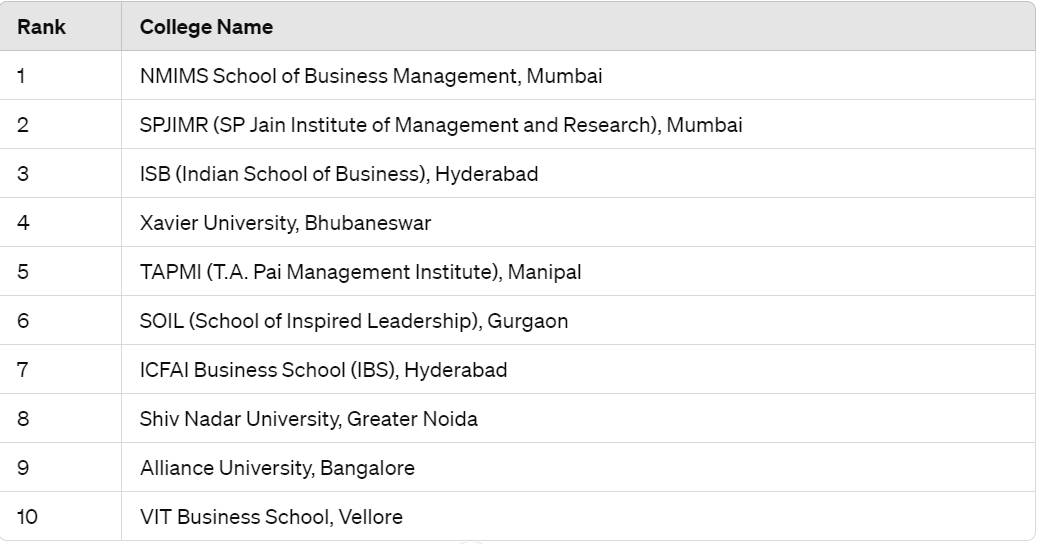
- CMAT: The CMAT consists of four sections: Quantitative Techniques and Data Interpretation, Logical Reasoning, Language Comprehension, and General Awareness. The exam is conducted in a single three-hour session, and there are 100 multiple-choice questions in total.
- NMAT: The NMAT is also divided into three sections: Language Skills, Quantitative Skills, and Logical Reasoning. The exam is conducted over a period of 75 days, and candidates have the flexibility to choose their test date and time within this window. The total number of questions and time allotted for each section may vary.
- Exam Conducting Body:
- CMAT: The CMAT is conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA), which is responsible for organizing various national-level entrance exams in India.
- NMAT: The NMAT is conducted by the Graduate Management Admission Council (GMAC), which is the same organization that conducts the GMAT (Graduate Management Admission Test) worldwide. Also Read:MBA ADMISSIONS : CHOOSING BETWEEN BUSSINESS SCHOOLS
- Accepting Institutes:
- CMAT: CMAT scores are accepted by a wide range of management institutes across India, including universities, colleges, and autonomous institutions.
- NMAT: NMAT scores are primarily accepted by NMIMS (Narsee Monjee Institute of Management Studies) and its associated colleges. However, in recent years, some other leading B-Schools in India have also started accepting NMAT scores for their admissions.
5.Test Duration:
- CMAT: CMAT is typically conducted within a duration of three hours.
- NMAT: NMAT allows a time window of about two months for candidates to schedule their exam. The actual test duration is around two hours.
6.Frequency:
- CMAT: CMAT is usually conducted once a year.
- NMAT: NMAT is conducted over a specified period of about two months, allowing candidates to choose their preferred exam date within that window.
7.Scoring Pattern:
- CMAT: CMAT scores are scaled from 100 to 400, with higher scores indicating better performance. Negative marking applies for incorrect answers.
- NMAT: NMAT scores are reported on a scale from 0 to 360. There's no negative marking, so candidates are encouraged to attempt all questions.
Also read : MBA Interview Tips and Resources
CMAT EXAM PATTERN
TOP 10 COLLEGE'S LIST FOR CMAT

NMAT EXAM PATTERN
TOP 10 COLLEGE'S LIST FOR NMAT